Assessment is a fundamental part of education. It helps teachers understand how well students are learning. While classroom activities, quizzes, and discussions help track progress during lessons, teachers also need a clear way to evaluate learning at the end of a unit or course. This is where summative assessment is used.
Summative assessment focuses on measuring what students have learned after instruction is complete. It is often used for final exams, projects, or evaluations that contribute to grades or academic decisions. These assessments help teachers check whether learning goals have been achieved and give students a clear picture of their performance.
In this article, you will learn what summative assessment is, why it is important, and see easy-to-understand summative assessment examples used in different educational settings.
What is Summative Assessment?
Summative assessment is a type of assessment process used to measure students’ learning and knowledge at the end of a unit, term, semester, or course. Its primary purpose is to determine what students have learned and whether they have met the defined learning objectives or standards.
Unlike formative assessment, which focuses on ongoing feedback and improvement, summative assessment focuses on final outcomes. It is often graded and contributes to final results, promotion decisions, or certification. In simple terms, summative assessment can be described as an assessment of learning, as it answers the question: What did the student learn by the end?
The key features of summative assessment include:
It is conducted only after instruction or learning has been completed.
It measures specific learning objectives and curriculum standards.
It is typically high-stakes or graded in nature and often contributes to final grades.
It follows a structured and consistent format to ensure fairness for all students.
It focuses on final achievement rather than the learning process itself.
Explore 8 Common Summative Assessment Examples
Check out the most common summative assessment examples explained clearly so you understand how and why they are used.
1. End-of-Term or Final Examinations
End-of-term or final examinations are one of the most traditional and widely recognized forms of summative assessment. These exams are typically administered at the conclusion of a semester, term, or academic year to evaluate how well students have mastered the full range of content taught over that period.
Final exams usually consist of a structured set of questions such as multiple-choice items, short answers, essays, or problem-solving tasks, depending on the subject and grade level. They are designed to measure cumulative understanding rather than day-to-day progress.

Teachers use end-of-term exams to make high-level decisions such as assigning final grades, determining promotion or placement, and evaluating overall instructional effectiveness. Because these exams summarize learning outcomes, they provide a clear snapshot of what students know and can do at the end of instruction.
2. Standardized Tests
Standardized tests are large-scale summative assessments used to compare student performance against common benchmarks. These tests follow strict guidelines and use consistent scoring systems to ensure fairness. For example, board examinations, college entrance tests, language proficiency exams, etc.
These assessments are often used for admissions, certifications, and policy decisions, making them high-stakes for students.
3. Chapter or Unit Tests
Unit or chapter tests are conducted after finishing a specific topic or section of a subject. Rather than testing the whole course, they focus on a smaller portion of the curriculum at a time. This helps teachers quickly check whether students have understood the main ideas before moving on to the next topic.
But in classrooms, unit tests can be tricky to manage. Writing balanced questions takes time, and using the same few question types does not always show what students truly understand. Grading and reviewing results can also be slow and tiring, especially in larger classes.
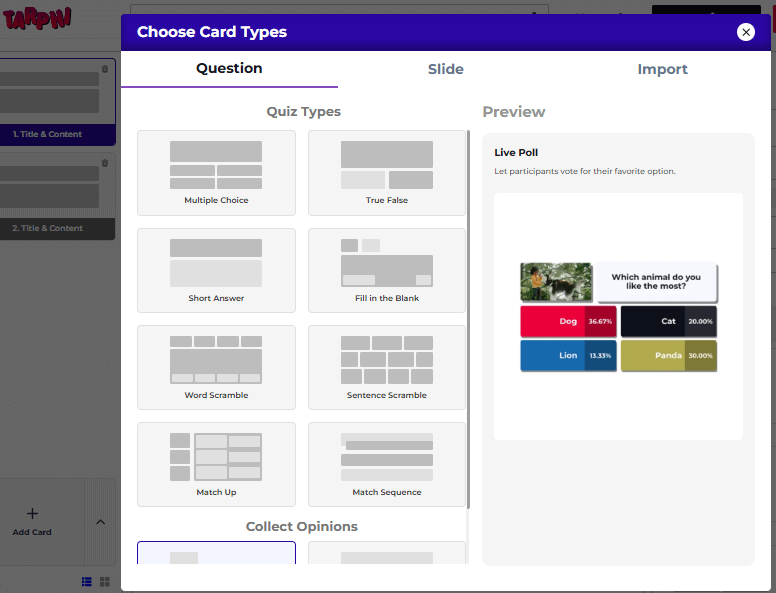
Here, Tarphi helps make the whole process easier and faster. Teachers can choose from 8 different question types to assess from different angles on that specific topic. Using AI, they can turn lessons or class lectures into curriculum-aligned unit tests in minutes. Once the test is complete, Tarphi instantly generates clear reports highlighting correct/incorrect answers. Based on this, teachers can grade them quickly.
4. Final Projects
Final projects are a more practical and engaging type of summative assessment. Instead of answering questions on paper, students apply what they have learned to complete a task or create a product. This might include a research project, a science experiment, a presentation, or a real-world problem-solving activity.

Final projects allow students to demonstrate deeper understanding, creativity, and critical thinking, making them an effective alternative to traditional exams.
5. Portfolios
Portfolios are collections of student work submitted at the end of a learning period for final evaluation. They may include essays, reports, artwork, reflections, or project samples created over time. Portfolios work well as summative assessments because they show both achievement and growth.
In this assessment, teachers can see not just what the student produced, but how their skills and understanding developed throughout the course.
6. Formal Essays
Formal essays are commonly used as summative assessments in subjects such as literature, history, and social sciences. In an essay-based assessment, students are asked to explain concepts, analyze ideas, or argue a position using evidence. Essays help teachers evaluate a student’s depth of understanding, reasoning ability, and communication skills, rather than just memorization.
7. Oral Examinations or Presentations
Oral examinations and presentations assess learning through spoken responses rather than written ones. Teachers may ask students to explain a topic, present a project, or answer questions verbally. These assessments are particularly useful for evaluating communication skills, conceptual clarity, and confidence. They are often used in language learning, professional training, and higher education.
8. Open Book Exam
In an open-book exam, students are allowed to use textbooks or notes while answering questions. This may seem easier, but the real purpose is to test how well students understand ideas and apply what they have learned rather than test memory.
Sometimes, open-book exams can be difficult to manage. When questions are too simple or time is not controlled, students may just copy answers without really understanding them. This makes it difficult for teachers to judge real understanding.
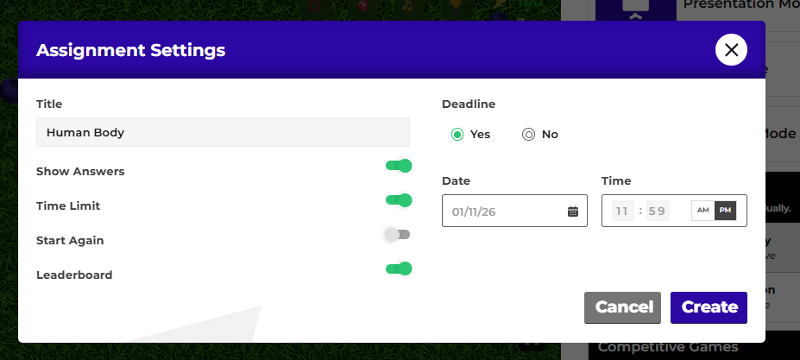
This is where Tarphi makes open-book exams more effective. Teachers can create structured digital assignments with different question types and control settings like time limits, deadlines, retakes, and answer visibility. With limited time and retakes turned off, students do not get enough time to search answers from books or AI, even though it is an open-book exam.
Teachers can also include videos directly inside questions and ask students to respond based on what they watch. Since students must watch the video carefully to answer within the time, they cannot simply search for answers in books or notes. So this encourages students to prepare perfectly for the exam.
After the assessment, Tarphi provides clear performance reports, making it easy for teachers to review results, compare scores, and create final grade sheets. As a result, open-book exams become more meaningful, fair, and effective.
Tarphi: Your All-in-One Solution for Summative Assessment
For summative assessments to be effective, teachers need flexibility in question design and clarity in evaluation. A single test format is often not enough to measure learning accurately. Tarphi addresses this by offering 8 different question types, such as Multiple Choice, True/False, Short Answer, Fill in the Blank, Match Up, Match Sequence, Word Scramble, and Sentence Scramble. This variety allows teachers to assess understanding from multiple angles, not just memorization.
Because summative assessments are graded, clear and reliable reporting is essential. Tarphi automatically generates student-level and question-level reports, making it easy to see scores, accuracy, and performance patterns, without spending hours reviewing papers. This makes Tarphi well-suited for formal evaluations.
How summative assessment works in Tarphi
Imagine a teacher sets an assignment, adjusts settings like time limits, retakes, or deadlines, and assigns it to students. Once students complete the assessment, Tarphi generates a detailed report that can be exported and added directly to a gradebook for easy record-keeping.
Tarphi also supports AI-powered quiz creation aligned with grade level and curriculum needs. This saves time while ensuring assessments match learning goals and standards.
Overall, Tarphi simplifies summative assessment by combining flexible question types, grading control, and clear reporting in one easy workflow.
Benefits of Summative Assessment
Summative assessment offers several important benefits that make it a valuable part of the learning and evaluation process. One of its biggest advantages is that it provides clear and measurable evidence of learning. By the end of a course or unit, teachers can see exactly what students have understood and how well they have met the learning objectives.
Another key benefit is that summative assessment supports fair and structured grading. Because these assessments are aligned with curriculum standards and use consistent criteria, they help ensure that all students are evaluated equally. This clarity also helps students understand how their performance is judged.
Summative assessments also help identify strengths and learning gaps. When teachers review results, the patterns show which topics students mastered and where they struggled. This information is useful for improving future lessons, adjusting teaching strategies, or revisiting difficult concepts.
In addition, summative assessment encourages student responsibility and preparation. Knowing that their learning will be evaluated at the end of a unit often motivates students to review content, stay focused, and take ownership of their learning.
Finally, summative assessments prepare students for real-world evaluations. Many academic and professional situations, such as entrance exams, certifications, and job assessments, follow a summative format. Regular exposure to structured assessments helps students build confidence and exam readiness over time.
Limitations of Summative Assessment
Despite its advantages, summative assessment also has some limitations that teachers should consider. One common challenge is that it can create stress and anxiety for students. Because these assessments are often graded and high-stakes, some students may feel pressure that affects their performance.
Another limitation is that summative assessment focuses mainly on final outcomes, not the learning process. It does not always show how much effort a student made, how their understanding developed over time, or how much progress they achieved during instruction.
Summative assessments may also provide limited feedback. When results are shared only as scores or grades, students may not clearly understand their mistakes or how to improve. Without detailed feedback, the assessment’s value as a learning tool can be reduced.
In addition, relying too heavily on summative assessment can limit flexibility in teaching. If instruction is focused only on final tests, it may overlook individual learning needs or different learning styles.
For these reasons, summative assessment works best when combined with formative assessment. While summative assessment evaluates what students have learned at the end, formative assessment supports learning along the way. Together, they create a more balanced, fair, and effective approach to assessing student learning.
Best Practices for Effective Summative Assessments
Be clear about what you want to assess: Before creating a summative assessment, it’s important to be clear about the skills or knowledge you are measuring. Clear goals make the assessment more focused and meaningful.
Mix different types of questions or tasks: Using a variety of formats helps students to demonstrate understanding in different ways and gives a more accurate picture of understanding.
Use rubrics to keep grading fair: Rubrics create consistency and help both teachers and students understand how work is evaluated.
Keep assessments aligned with the curriculum: The assessment should reflect the curriculum, what was actually taught, not surprise students with unrelated content.
Give clear instructions from the start: Clear instructions reduce confusion and help students focus on the task.
Review results to improve teaching: Assessment results provide useful insights into student learning. Reviewing them helps you identify the gaps and refine your lessons.
Conclusion
So far, you have learned what summative assessment is, how it works, and the different ways it can be used to measure student learning. From final exams and unit tests to projects, portfolios, and presentations, summative assessments help teachers evaluate learning outcomes clearly and fairly. When designed with the right methods and supported by tools like Tarphi for structured assessments and reporting, summative assessment becomes more than just grading and contributes to fair evaluation, effective teaching, and meaningful learning experiences.

Turn your lessons into interactive quizzes, games, and presentations.
No credit card required.